Every magician has a bag of tricks. Every mechanic has a bag of tools.
Whether you’re designing a network, diagnosing an anomaly, troubleshooting an issue, or monitoring an environment – your bag of Networking Tools and software should be complete, robust, and reliable.
This is why we’ve compiled a list of some of the Best Tools for Network administrators, at zero cost, to get you started.
Some will be familiar, some will be new.
Either way, this list should serve to either validate what you’re already using or supplement where you’re lacking.
Let’s dive in!
Here is our list of the best network admin tools for everyday troubleshooting:
- ManageEngine OpManager – EDITOR’S CHOICE A network, server, and endpoint monitoring system that is also able to manage the resource usage of hypervisors. Installs on Windows Server and Linux. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL This package excels at network monitoring with both device status monitoring and traffic flow analysis. It also monitors servers, cloud platforms, and applications. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Nagios An extensible, free network monitoring system, called Nagios Core with a paid version, called Nagios XI. Installs on Linux.
- Ntopng This is a free network traffic monitoring and analysis system. The software is free to use but the developers ask for a donation. Ntopng is available for Windows, Linux, macOS, Raspberry Pi, and Unix.
- Wireshark / Tshark A free network packet sniffer that is highly respected and widely used. The packet viewer enables protocol identification.
- iPerf / JPerf A free tool that measures the available bandwidth between two nodes on a network. Installs on Windows, Linux, Android, macOS X, and Unix.
- Nmap / Zenmap A network monitoring system that generates a range of data including IP address usage. Nmap is a command-line system and Zenmap has a GUI interface. Installs on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Paessler SNMP Tester A free tool that checks on all of the conditions needed for SNMP agents to work properly and communicate with the SNMP manager. Installs on Windows Server.
- Angry IP Scanner A free tool that gathers IP address usage data. This utility offers a lightweight IP address manager and also a port scanner. Installs on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Ansible A task automation system that enables administrators to create playbooks, that act as workflows to complete mundane tasks. Runs on RHEL Linux.
- Netmiko A Python library that enables Python automation scripts to interact with network devices.
- Notepad++ / UltraEdit / Sublime Text Three text editors that are great for editing scripts and config files.
- Cygwin Implements well-known Linux commands on PCs at the command line.
- Draw.io A free, online diagramming tool that is great for creating ERDs and flow charts.
The Best Network Admin Tools & Software
Our methodology for selecting network admin tools and software
We reviewed various network admin tools and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- An autodiscovery system to log all network devices
- A network topology mapper
- The ability to collect live network devices statuses by using SNMP
- A facility to analyze network performance over time
- Graphical interpretation of data, such as charts and graphs
- A free trial period, a demo, or a money-back guarantee for no-risk assessment
- A good price that reflects value for money when compared to the functions offered
Monitoring & Logging
1. ManageEngine OpManager – FREE TRIAL
“An infrastructure monitor that covers network device and server statuses”
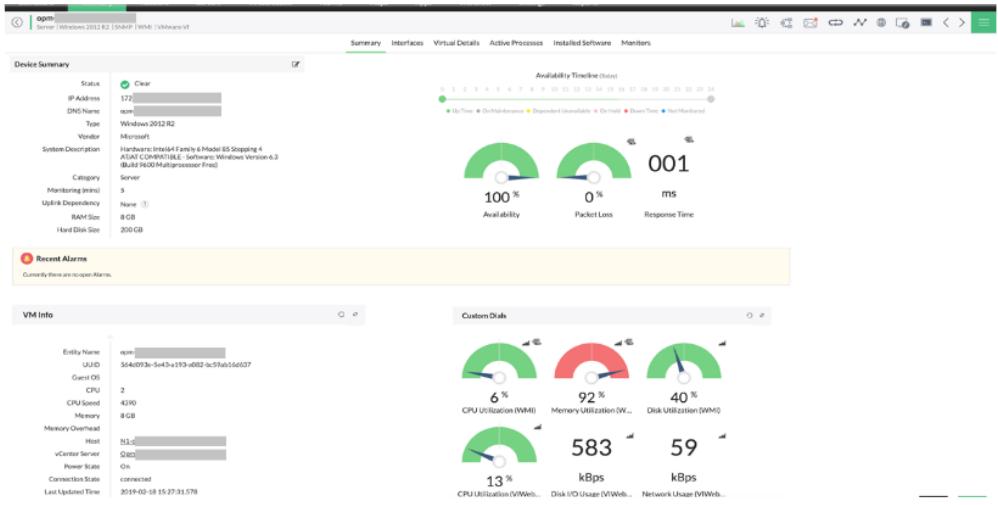
While many monitoring systems separate network performance monitoring and server monitoring out into two separate packages, OpManager combines the two in one purchase. This tool also covers some key applications, such as virtualizations.
Key Features:
- Monitors networks and servers
- Uses SNMP
- Alerts for device faults
- Can run on AWS or Azure
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine OpManager implements performance monitoring for networks and servers. The service implements continuous network discovery that generates an inventory and network topology map. This system is based around the simple Network Management Protocol and it receives regular status reports from network devices, warning of potential faults.
OpManager uses a threshold system to identify when performance is likely to get impaired. There are many little problems that can soon stack up to bring performance to a level of impairment that users will notice. Catching these problems when they first arise gives you a chance to take action to head off disaster.
If a performance threshold gets crossed, the OpManager system generates an alert. This is shown in the service’s dashboard but it can also be forwarded to key personnel by SMS message or email.
OpManager is available in a free version. This has all of the functionality of the paid edition, but it is limited to monitoring only three devices. Those interested in the paid version have three choices of plans: Standard, Professional, and Enterprise. All versions are available for installation on Windows Server and Linux.
Who is it recommended for?
This package has a Free edition but it is limited to monitoring just three devices. The minimum coverage by the paid editions is for 25 devices. There is also an edition for managed service providers that includes a multi-tenant architecture.
Pros:
- Can monitor bandwidth consumption as well as alert to configuration changes that could impact network performance
- Can monitor bandwidth and resource consumption on the application level, and even drill down to identify specific users consuming the most resources
- Supports email, SMS, and webhook for numerous alerting channels
- Integrates well in the ManageEngine ecosystem with their other products
Cons:
- Takes time to fully explore all the options available in the ManageEngine software suite
Download:
Access a 30-day free trial of ManageEngine OpManager
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine OpManager is our top pick for a free network admin tool for everyday troubleshooting because it offers a comprehensive set of monitoring and diagnostic features without the need for a paid subscription. Designed to simplify network management, OpManager provides network administrators with essential tools for quickly identifying and resolving common network issues, making it ideal for daily troubleshooting tasks. The free version of OpManager includes a wide range of features, such as real-time network device monitoring, interface monitoring, and SNMP-based management. It provides instant alerts and notifications whenever there are performance anomalies, allowing IT teams to act quickly. OpManager’s user-friendly interface makes it easy to visualize network performance and pinpoint issues like device outages, network congestion, or bottlenecks. This level of visibility is essential for addressing everyday troubleshooting challenges. OpManager also includes key troubleshooting tools such as ping, traceroute, and route analysis, which help administrators assess network connectivity and diagnose issues with precision. The ability to generate real-time reports, track historical performance, and monitor device availability ensures that administrators can troubleshoot effectively and proactively prevent recurring issues. System managers who want to get the full OpManager package without paying can access the free trial.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/network-monitoring/download.html
OS: Windows Server, Linux, AWS, and Azure
2. Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL
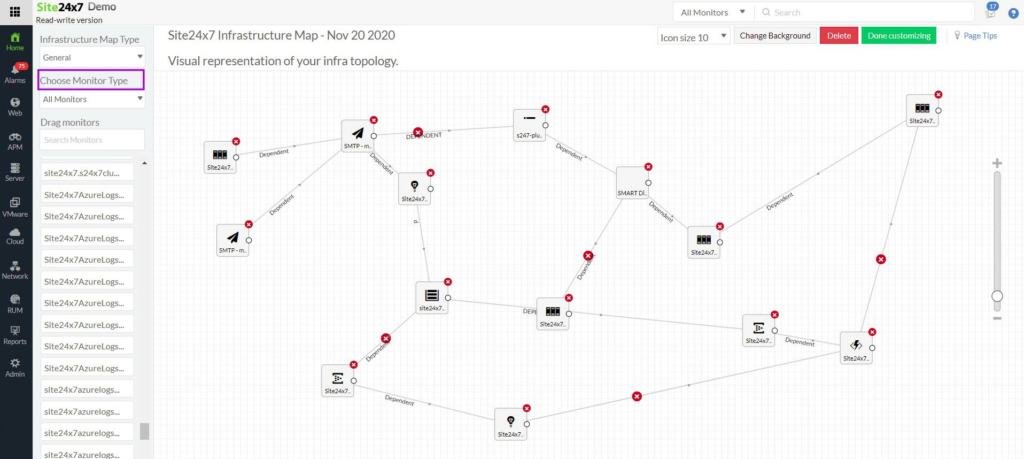
Network monitoring is the core unit on the Site24x7 cloud platform. This module includes network discovery and inventory management. The package will also create a network map, which is a great aid for network administrators when troubleshooting problems. The package will automatically monitor all network devices continuously and raise an alert if a component error occurs. The package also includes traffic flow analysis functions.
Key Features:
- Network discovery
- Network inventory and map
- Connection testing utilities
Why do we recommend it?
Site24x7 is an excellent network administration tool for everyday troubleshooting. It offers IT teams a comprehensive suite of monitoring and diagnostic features to resolve network issues quickly. With real-time network performance monitoring, it provides detailed insights into network traffic, latency, device health, and bandwidth usage, allowing administrators to identify performance bottlenecks, misconfigurations, or connectivity issues in real time.
The platform supports multi-layered troubleshooting by tracking key network parameters like DNS, HTTP, SNMP, and packet loss, providing a holistic view of network performance across diverse environments. This data is essential for network administrators to pinpoint issues affecting end-user experience and mitigate downtime.
Who is it recommended for?
We recommend Site24x7 for IT teams, network administrators, and system engineers in businesses of all sizes. It is particularly beneficial for organizations that manage complex or large-scale networks, where proactive monitoring and quick issue resolution are essential. The platform is ideal for businesses looking to streamline network performance management, minimize downtime, and ensure optimal network operation across distributed infrastructures.
Pros:
- Advanced diagnostic tools, such as route tracing, packet capture, and network path analysis
- Customizable alerts
- Generates detailed historical reports and trend analysis
Cons:
- No on-premises version
One of the things we like the most about Site24x7 is that it can monitor any network anywhere from its cloud platform. Thus, it is possible to unify the monitoring of networks on multiple sites in one Operations Center. The system is easy to set up and can be easily expanded thanks to its library of integrations. Get a 30-day free trial.
3. Nagios
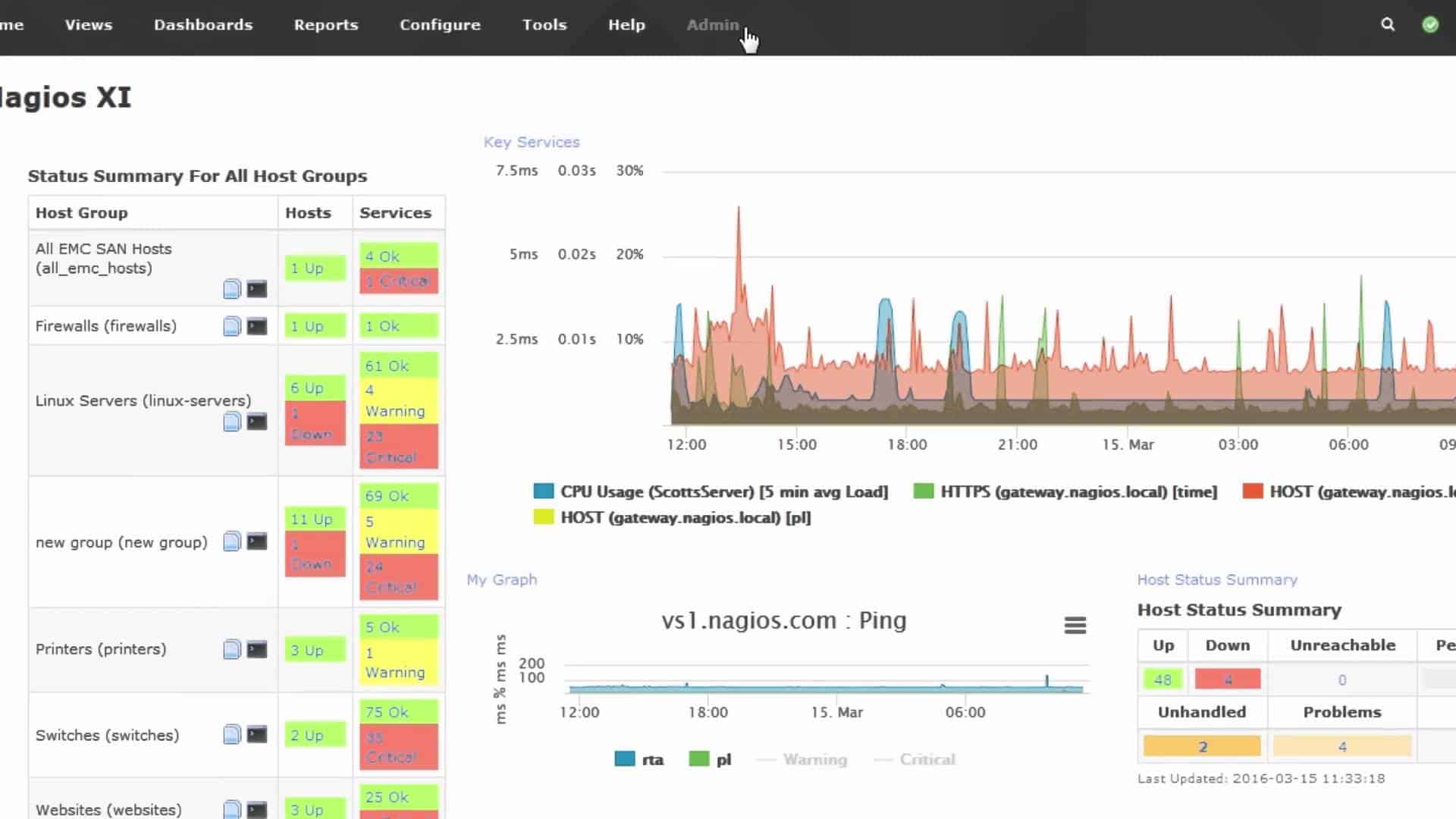
Nagios is a networking monitoring software solution. In fact, it’s a suite of solutions for monitoring network availability, analyzing data flows and security, as well as collecting logs for auditing. It’s completely open source and has a vibrant community of like-minded developers and administrators.
Key Features:
- Free and paid versions
- Runs on Linux or Docker
- Full stack monitoring
Why do we recommend it?
Look to Nagios Core for a free network monitoring system. This package won’t give you network traffic monitoring but it is a very competent network performance monitor. The tool will discover all of your devices and constantly monitor their statuses. The tool also monitors servers and applications.
With Nagios XI you can monitor everything from infrastructure to applications with granular detail. With Nagios Log Server, you can quickly sift through a central repository of audit logs, or setup triggers to alert you to critical events such as threats. And with Nagios Network Analyzer, dig deep into the health and integrity of your systems and network. Analyze flows, validate intent and troubleshoot with the lights on.
Who is it recommended for?
The Nagios Core package is very widely used and it is customizable. Businesses that need professional support packages for their software should look at the paid version, which is called Nagios XI. One problem is that neither version includes traffic analysis – that’s a separate package.
Pros:
- Open-source transparent tool
- Simple, yet informative interface
- Flexible alerting options support SMS and email
- Robust API backend makes it a great option for developers who want to integrate their own custom applications
- Very generous two-month trial period
Cons:
- Open-source version lacks quality support found
What I like most about Nagios is their straightforward approach to monitoring. They have multiple ways to represent data visually, which is another key interest of mine. Lastly, the built-in failover is wickedly cool if you start monitoring larger environments.
4. NTOPNG
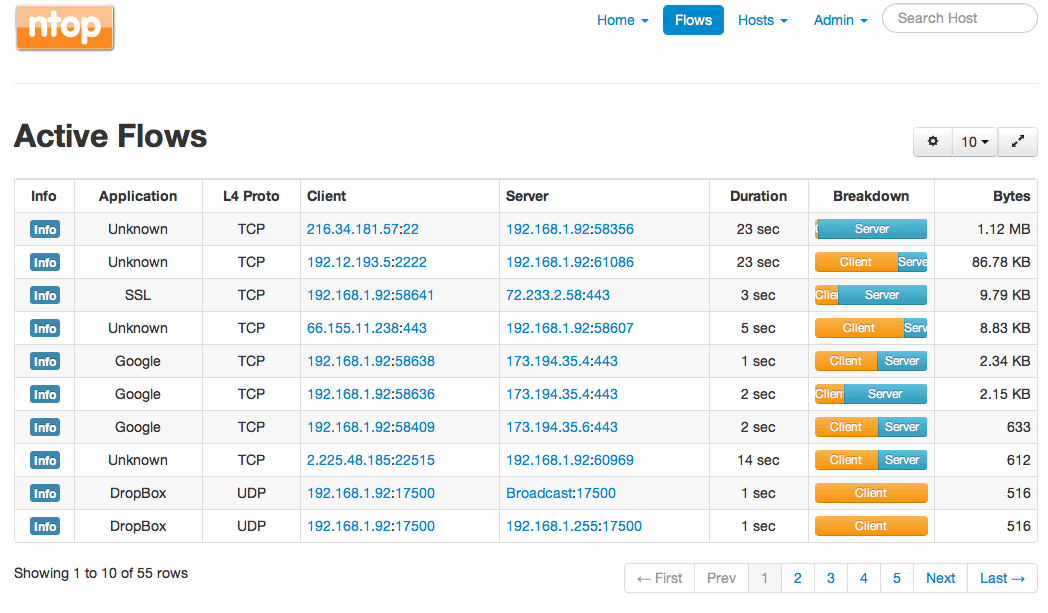
“High-Speed Web-based Traffic Analysis and Flow Collection.”
Named after the popular top command in Unix, ntop shows network usage similarly to how top shows system usage. Ntopng, based on libpcap, is the next generation version of the original ntop. It was written in a portable manner, which gives it the flexibility to run on numerous platforms: Linux, Mac OSX, and Windows.
Key Features:
- Packet sniffer
- Protocol analyzer
- NetFlow analysis
Why do we recommend it?
NtopNG is a free package that can be used just to extract packets from a network or you can use its full capabilities to read in NetFlow data from network devices and produce graphs, charts, and alerts from it. The system has two paid versions for companies with money.
Web-based, ntopng allows you to view traffic data and gather reports regarding network status. You can use numerous criterion for sorting, including IP address, ports, Layer 7 protocols, BGP AS, and so on. You can even do long-term reports to collect metrics such as throughput over time.
Who is it recommended for?
This free package is suitable for any network manager and is particularly useful for those who want to perform packet-level analysis. It can also be used to aggregate traffic data for alert creation. The service is available in two higher-paid editions, called Pro and Enterprise.
Pros:
- Open-source project with full transparency
- Free version available alongside the enterprise version
- Special licensing options for nonprofits and educational institutions
Cons:
- User interface is easy to use, but could be improved upon
I personally use this tool to generate detailed host-based reports showing applications latency, RTT, TCP statistics like retransmissions, out-of-orders, and zero windows.
Analysis
5. Wireshark / Tshark
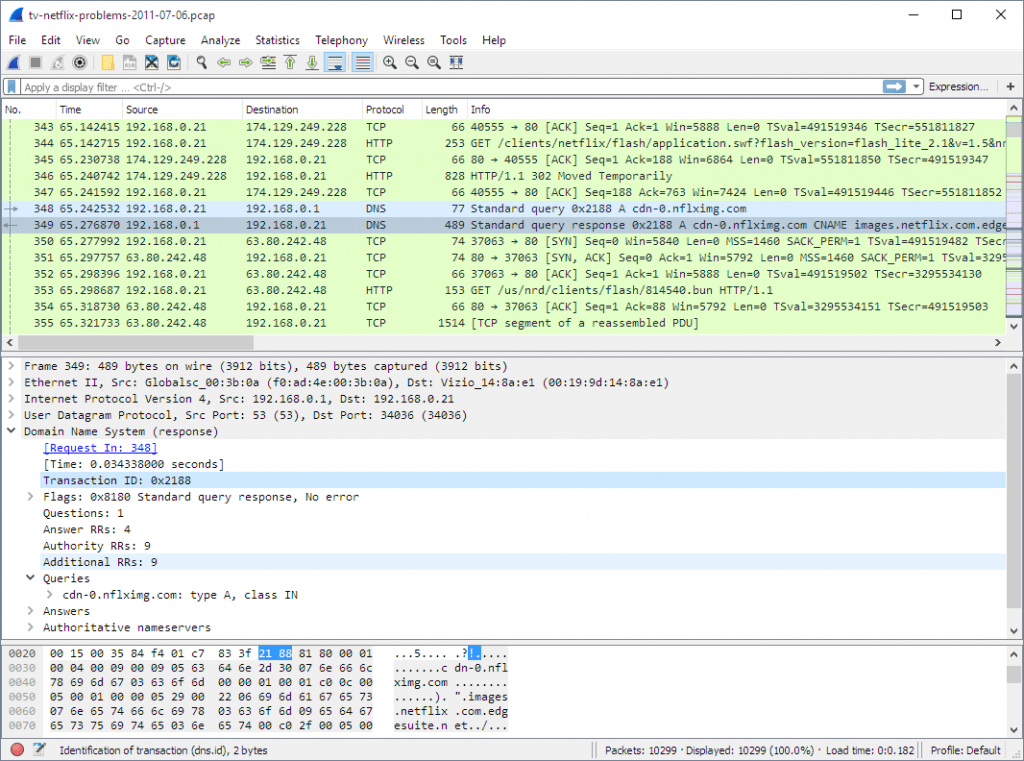
This is a no-brainer for most but needs to be mentioned for integrity’s sake.
Wireshark is an unparalleled network protocol analyzer, and honestly, one of the best free network tools ever made.
When you’re troubleshooting an issue and actually need to get into the weeds to find out what’s going on – this is your microscope. Never leave home without it!
Key Features:
- Packet capture
- Packet type color coding
- Filters and query language
Why do we recommend it?
Wireshark is a great package analysis tool. It can be used for performance analysis and security scanning, and it is also frequently used by hackers and penetration testers. This is a free tool and it has its own query language, so the tool has a highly skilled and extensive user community of network technicians.
Who is it recommended for?
All network managers should get this tool. If you have done a network management or cybersecurity course, you have probably already been taught how to use Wireshark and you probably already have it. The proprietary filtering and query language takes a lot of time to learn.
Pros:
- Massive open-source community keeps the software updated and new features are added periodically
- Built by network professionals, for network professionals
- Can save captured packet data for further analysis or archival purposes
Cons:
- Collects massive amounts of data by default – must be sorted and filtered
If you’re looking for some command-line capturing, or maybe you want to programmatically trigger packet captures, don’t forget to check out TShark. It’s included with Wireshark, and totally awesome.
6. iPerf / JPerf
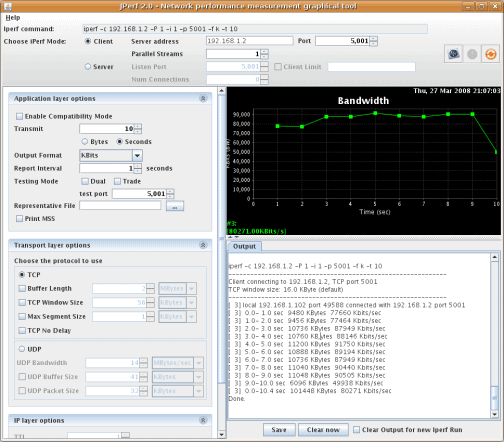
Between any two nodes is a network – be it vast or small. A simple ping between the two nodes is only good for general reachability and understanding the round-trip time for the small packets. If you want to measure actually achievable bandwidth, you need another tool such as iPerf.
Key Features:
- Notes total capacity and usage per link
- Identifies capacity problems
- Helps with capacity planning
Why do we recommend it?
iPerf gives you a traffic sampling service and JPerf is a GUI version of the tool. You can check on bandwidth availability with this tool, letting it run tests on capacity utilization periodically. This is a useful service that you can set up to run in the background and trigger alerts.
iPerf3 is the latest iteration of this tool. You run the client on two ends of a network, configuring the parameters needed to measure performance. It supports tuning of many parameters related to timing, buffers, and protocols (TCP, UDP, SCTP with IPv4 and IPv6). Upon execution, it actively measures and reports on bandwidth, loss, latency, jitter, and so on. You can initiate multiple simultaneous connections to truly simulate load across the network. Very handy tool!
Who is it recommended for?
This is a rudimentary traffic capacity checker and it would be suitable for a small business network. The tool essentially checks on a path to a destination, which means that you would have to launch a lot of queries to get all paths across your network test simultaneously.
If you’re more of a GUI person, check out Jperf. It’s up there in age but still works like a champ.
Pros:
- Accurately notes total capacity and usage per link
- Effectively identifies and aids in resolving capacity problems
- iPerf3 supports multiple protocols and parameters
- Allows for simultaneous multiple connections for network load simulation
Cons:
- Primarily suited for small business networks
- Requires multiple queries for comprehensive path testing
- JPerf’s interface may feel outdated for some users
7. Nmap / Zenmap
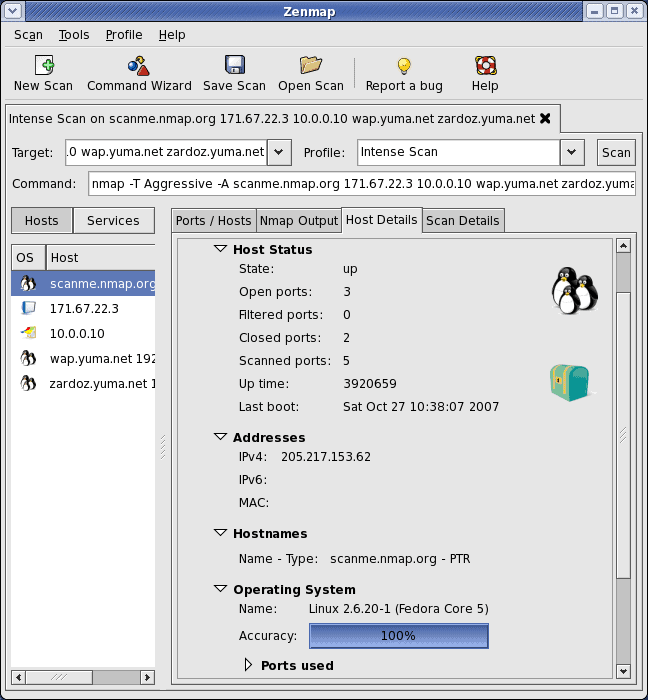
I personally use Nmap at least once a week. Almost verbatim from their website: Nmap (Network Mapper) is a security scanner used to discover hosts and services on a computer network, thus creating a “map” of the network. To accomplish its goal, Nmap sends specially crafted packets to the target host and then analyzes the responses.
Key Features:
- Powerful command line tool
- GUI with Zenmap
- Probe a network
Why do we recommend it?
Nmap is a command line tool for network exploration. It is a little dated but it is still one of the main tools use by network technicians for network investigations. It is a single command but it can perform a lot of different queries depending on which options you implement with it.
Nmap provides an incredible number of features for probing networks, including host discovery, service discovery and operating system detection. These features are extensible by scripts that provide more advanced service detection, vulnerability detection, and other features. In fact, Nmap is used in the backend for various security assessment tools such as Nexpose.
Who is it recommended for?
Nmap is used by network technicians, hackers, and penetration testers. It is a very highly respected tool and you will be taught how to use it if you do a network management or cybersecurity course. Learn what all the options do to get the best out of the system.
Pros:
- Doubles as a security tool, allowing administrators to discover open ports, and applications communicating over ports that are suspicious
- Massive open-source community, is one of the most popular free security tools available
- Offers a GUI version, Zenmap, which lowers the barrier to entry for new users
- Syntax is straightforward and not difficult to learn for most users
Cons:
- Nmap can have a steep learning curve for new users
- Might be overkill for simpler troubleshooting tasks
Again, if you’re more a fan of GUIs, make sure the download the bundle with Zenmap.
8. Paessler SNMP Tester
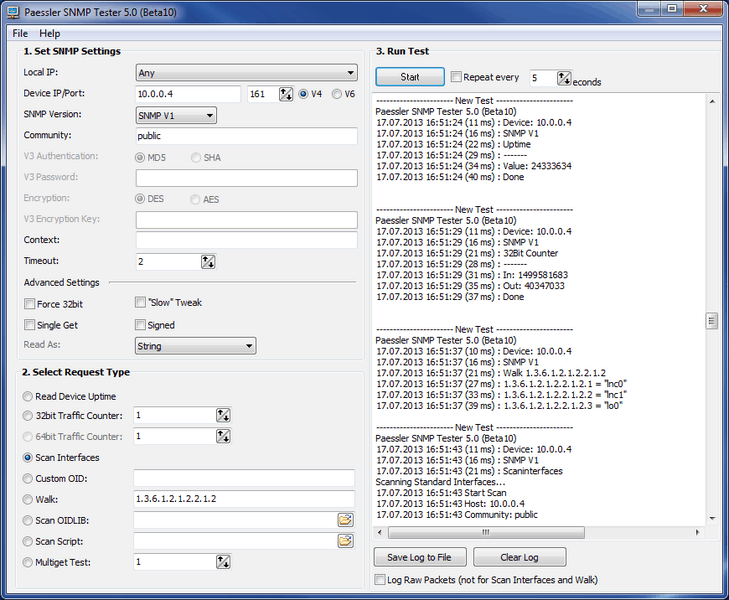
SNMP can be hard. This is why you need a good tester. There are a few out there, but I’ve found great success with Paessler’s SNMP tester.
Key Features:
- Standalone utility
- Checks on SNMP
- Also tests network links
Why do we recommend it?
Paessler SNMP Tester is a useful tool for network managers who are setting up a monitoring system. If you want to check whether an SNMP device agent is turned on, you can use this tool. The tool is free to use and it runs on Windows.
Who is it recommended for?
An extra benefit of the tool is that you can check whether a device that you expect to be using a specific IP address is actually there. Paessler also offers PRTG, which is a much larger SNMP-based tool and that package will discover all of your SNMP-enabled devices.
Pros:
- Great tool for prepping devices for a SIEM implementation or other agent-based monitoring
- Super lightweight, doesn’t take up much space or system resources
- Works well in tandem with other PRTG sensors
Cons:
- PRTG is designed for network administrators and requires networking knowledge to fully utilize
The idea of this program is to have a tool that enables the user to debug SNMP activities in order to find communication and/or data problems in SNMP monitoring configurations. Are your devices configured properly? Are you using the correct keys? Use this tool to validate if your SNMP configuration will function with programs like PRTG Network Monitor.
9. Angry IP Scanner
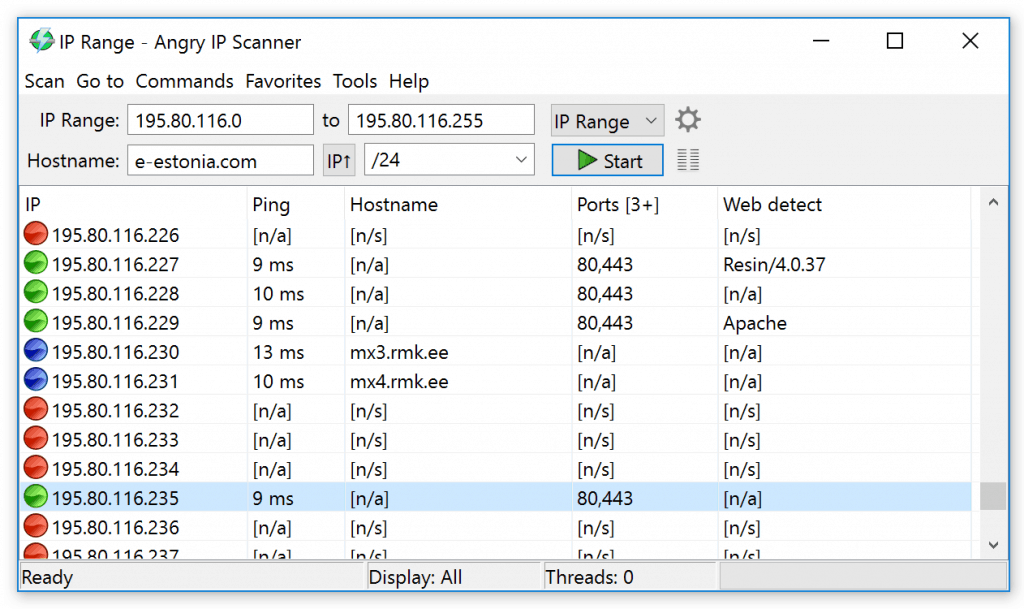
Angry IP scanner is an open-source, multi-threaded IP address and port scanner. Similar to Nmap, and used by millions, it’s become a standard tool for network admins. Angry IP Scanner first rapidly pings, then checks port status, then starts resolving hostnames, gathering MAC addresses, OSs and whatever it can discern based on the data gathered. It can collect NetBIOS info like workgroup and domain names, as well as logged-in users if you happen to have to privileged rights to retrieve this information. Like Nmap, it’s extensible with plugins. Scanning results can be saved to CSV, TXT, XML or IP-Port list files.
Key Features:
- IP scanner
- Port checker
- Ping tester
Why do we recommend it?
Angry IP Scanner is a very popular free tool and it has been downloaded 30 million times. The utility will scan an IP address range and you can make the range wide enough so that the tool will discover all of the devices on your network. You can also choose to focus on just one device.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is useful for anyone. It has a wide appeal because it will run on Windows, macOS, and Linux. The tool has a nice color-coded circle at the beginning of each line in its results that makes instant response status recognition possible. That rating refers to the results of a Ping test to that device.
Pros:
- One of the easiest tools to use on the market
- Great for small networks and home use
- Provides simple log outputs
- Lightweight tool – uses little system resources
Cons:
- Not ideal for continuous monitoring
- Lacks graphing capabilities
Runs on Windows, Mac, and Linux. Get it here.
Configuration & Transfers
10. Ansible
“No one likes repetitive tasks.”
Ansible is a simple and powerful automation engine with the goal of reducing repetition by automating tasks. It’s vendor agnostic, programmable and relatively easy to learn. The folks at Ansible believe that automation shouldn’t be more complex than the tasks it’s replacing.
Key Features:
- Task automation
- Flexible tool
- Time or event triggers
Why do we recommend it?
Red Hat Enterprise Ansible isn’t specifically a network management tool, it is a workload automation system that you can use to automate network administration tasks. The abilities of this tool extend to managing Active Directory, processing data with file movements, or data validation checks.
From a network perspective, I like this tool for generating configuration files based on my custom templates. I can quickly build “playbooks” for a large number of scenarios, ensuring that my configuration files are properly built based upon my standards and that my network devices are configured accordingly.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is able to implement processes on cloud platforms and different sites, not just on a single LAN. This makes it a very powerful tool for system designers as well as for network managers. The only problem is that you need to dedicate time to learning the tool in order to construct tools to save you time.
Pros:
- Simple minimalistic interface – makes it easy to view key metrics
- Leverages playbooks to automate device configuration and deployments
- Supports numerous vendors, with plenty of community-built template
- Completely open source and free
Cons:
- Is a full-service monitoring platform that can take time to fully explore all options available
- Open source tool that might not be the best fit for all network environments
If you want to get more with a GUI, check out Ansible Tower. Super clean.
11. Netmiko
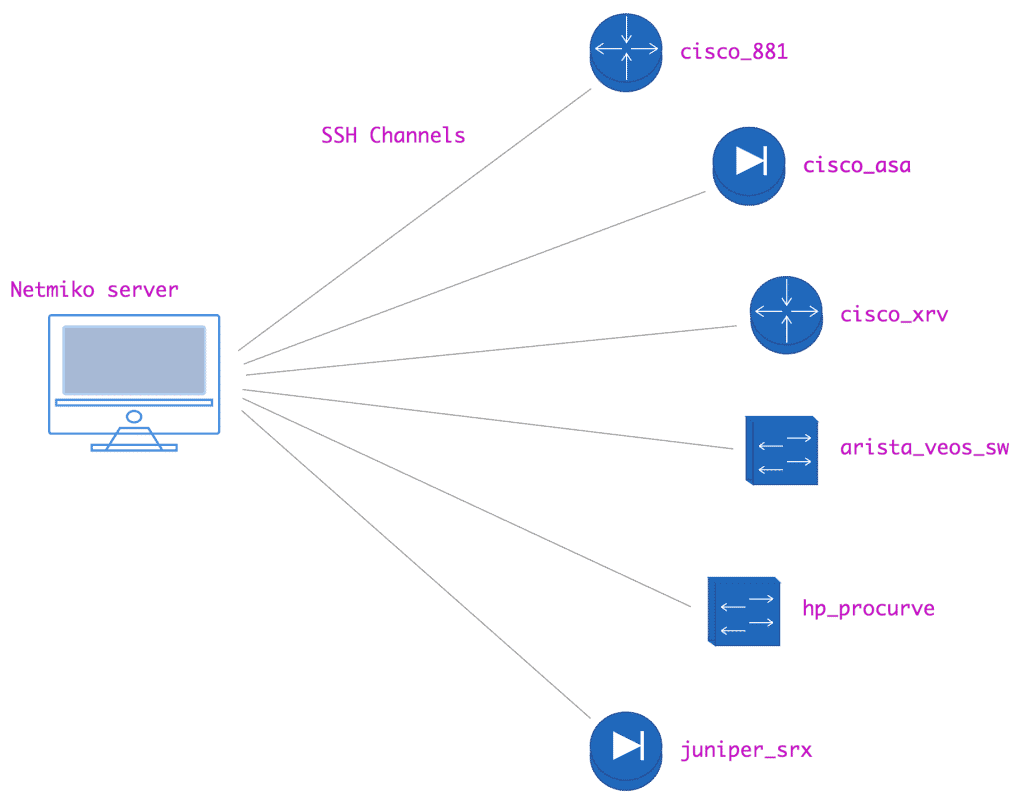
Created by Kirk Byers, Netmiko is a multi-vendor Python library that simplifies Paramiko, gearing it toward network devices. This is a more advanced tool, and only beneficial if you’re using Python for scripting or automation. It simplifies SSH connections, command execution and data retrieval like no-one’s business.
Netmiko current supports the following platforms:
- Cisco IOS, IOS-XE, IOS-XR, ASA, NX-OS, and WLC (with limited testing)
- Arista EOS
- HP ProCurve
- HP Comware (limited testing)
- Juniper Junos
- Brocade VDX (limited testing)
- F5 LTM (experimental)
- Huawei (limited testing)
Key Features:
- Secure connection
- Remote access to network devices
- Support device management
Why do we recommend it?
Netmiko Is a library of tools, written in PHP that lets you set up a secure connection to one of your network devices. You can contact your own network devices across your network anyway, so this tool would only be of use to connect to devices on another site, or to your single site from your home.
Who is it recommended for?
Anyone can use this tool to test switches and run show commands to gather settings. The package doesn’t add much to the usual switch command line service other than creating a secure connection from a remote location.
Pros:
- Lightweight SHH-based tool
- Ideal for users who are looking for a CLI automation tool
- Features an extensive library of supported vendors
Cons:
- Not as beginner-friendly as other tools that offer both GUI and CLI options
Each vendor has their own quirks regarding shell interaction. Whether is privileged modes, expert modes or commit functions, Netmiko is designed to simplify this lower-level SSH management across a wide set of networking vendors.
Terminals & Text Editors
12. Notepad++ / UltraEdit / Sublime Text
If you’re still using regular old Notepad, you have no idea what you’re missing out on. Step up your text game with one of these text editors. I guarantee you will not regret it!
Key Features:
- A selection of advanced editors
- Provides line numbers
- Code formatting
Why do we recommend it?
You are always going to need a lightweight editor to write scripts and programs and these three free options are worth looking into. Notepad++, UltraEdit, and Sublime Text don’t use much processor power, so you won’t drag down your CPU by having it open or even having multiple instances open simultaneously.
Who is it recommended for?
The tools are useful to have to hand. These are just three examples of text editors that are worth using. Take a look for others. For example, you might prefer a system that is based online or one that is portable that you can store on a memory stick.
Pros:
- Great for editing codes, PHP files, and configurations
- Can highlight syntax and help streamline edits
- Is aesthetically better than Notepad
Cons:
- Not a dedicated monitoring tool
We use Notepad++ Every single day – whether we’re editing PHP files, Nagios Configs, or Searching through Multiple files for a string or Text at the same time, Notepad++ is the best text-editor on the market!
13. Cygwin
If you’ve ever used Linux, you’ve become familiar with useful commands such as ‘grep’, ‘ls’, ‘top’, ‘df’, ‘pwd’ and so on. In the Windows world, we are missing some of these commands, and we have them, it’s written in some other non-intuitive syntax. Wouldn’t it be great to have Linux commands and applets in Window? Enter Cygwin.
Key Features:
- A collection of Linux tools
- For use on Windows
- Open source project
Why do we recommend it?
Cygwin is an ever-expanding source of utilities. Although the tool provides a way to run Linux commands on Windows it isn’t a virtual platform to run any Linux software on Windows. So, the package has limitations and isn’t quite as widely useful as many people think.
Who is it recommended for?
Cgywin provides Linux utilities for Windows. If you are used to working on Linux and now have to use Windows computers, you will miss the old commands that you regularly use. So, in this case, you would welcome the opportunity to get these familiar commands back.
Pros:
- Open-source transparent project
- Allows Linux applications to run inside Windows through recompling
- Is one of the only few backwards compatible options from Linux to Windows
Cons:
- Not as user-friendly as other options, has a steep learning curve
- Recompiling some applications from Linux to Windows doesn’t always work on the first attempt
Cygwin is a large collection of GNU and Open Source tools, which provide functionality similar to a Linux distribution on Windows. Not only can you run familiar commands, but also you can load (similar to apt-get or yum) various Linux tools. Some favorites of mine are wget and curl. If I’m running Windows, I’m running Cygwin.
14. Draw.io
I love Visio. It’s undoubtedly the best tool for designing network diagrams. However, it can be expensive, and it only runs on Windows. As a Mac user, I run a Windows VM just so I can use Microsoft Visio. While this does function, I’ve recently started using Draw.io, a browser-based diagramming application. It’s awesome!
Key Features:
- Online tool
- No account needed
- Store to your own location
Why do we recommend it?
Draw.io gives you a designer canvas to create any type of chart or diagram and that includes network maps. You can’t import automated discovery data into this tool, so you have to draw up your maps manually. You don’t need to set up an account and you can save your designs to your own cloud drive account.
Who is it recommended for?
Draw.io is one of the few free diagramming tools that you can access online. It doesn’t include storage space but you just save to your own account on Google Drive, OneDrive, Dropbox, GitLab, GitHub, or your own hard drive.
Pros:
- Cloud-based diagram creations
- Easy to use – even if you’re not great at design
- Offers hundreds of different icons
Cons:
- Not a live reflection of your network – better for planning and presentation
Whether you’re building an engineering diagram or a network diagram, Draw.io has tons of templates to get you started. It connects to online storage environments like Dropbox and Google Drive for real-time saving. No more losing data. Again, it’s absolutely free, and something you can rely on for cloud-based diagrams that are shareable and exportable.
Network Admin Tools FAQs
What are some common features of network admin tools?
Common features of network admin tools include device discovery and inventory, network mapping, bandwidth monitoring, configuration management, and security analysis.
What are some common network admin tools?
Common network admin tools include SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, PRTG Network Monitor, and ManageEngine OpManager.
What are some benefits of using network admin tools?
Benefits of using network admin tools include improved network performance and reliability, increased security, and better visibility and control over network infrastructure.
How can network admin tools help with troubleshooting network issues?
Network admin tools can help with troubleshooting network issues by providing detailed information about network devices, identifying network bottlenecks, and detecting security threats.
What are some common challenges associated with using network admin tools?
Common challenges associated with using network admin tools include managing large and complex network environments, detecting and responding to security threats, and maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
How can network admin tools help with network capacity planning?
Network admin tools can help with network capacity planning by analyzing performance metrics and identifying trends to help plan for future resource needs.
What is the role of network admin tools in IT operations management?
Network admin tools are a core component of IT operations management for managing and monitoring network infrastructure. They are used by various IT operations management components such as network performance management and network security management.