Here is our list of the best WMI tools & software for Windows management instrumentation administration:
- Paessler PRTG – EDITOR’S CHOICE This package of monitoring tools includes a WMI receiver, which presents a summary and gives access to each individual notification. Available for Windows Server or as a SaaS platform. Get a 30-day free trial.
- WMI Explorer (CodePlex): Open-source tool which has been moved to GitHub that executes the query in the WMI database and produces results accordingly.
- WMI Explorer (Sapien): Allows users to explore local as well as remote machines through cached data and multi-threaded code.
- WMI Explorer (Marc van Orsouw): Known for its great interface and includes powershell-based VMI with GUI, and the best part, it can be run on a modern Windows server.
- PowerShell: Mainly a WMI interpreter that explains the meaning of code, value and other information.
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Windows Management Instrumentation, or WMI, is is a technology which enables easier management of Microsoft Windows-based servers and workstations. It collects and reports on configuration information about the computer using a standard interface. You get:
- Capabilities of WMI – In addition to viewing configuration information, WMI also can manipulate windows computers by setting configurations of the computer. WMI is not a centralized configuration engine, but rather a framework build to remotely view and set configurations of individual Windows computers.
- Historical Context – Before the advent of WMI in the mid-1990s, doing remote management of Windows computers was very difficult. The first implementation of WMI was rather limited, but this has changed to include support for a wide variety of hardware and software configurations.
- Comparison with SNMP – WMI is very similar to another network management protocol that most network administrations are familiar with: SNMP. Like SNMP, WMI is in the middle layer between management applications and scripts, and configuration settings on a server.
- Unique Features of WMI – However, unlike SNMP, WMI is designed from the ground up to support countless configurations items. This means that WMI can report on, and control, complex Windows configuration items like mount points.
Our favorite WMI tools are broken into two categories:
- Browsers and
- Manipulators
As the names support one category is for browsing WMI objects and the other is for making changes.
The Best WMI Monitoring Tools
There are countless WMI tools, but the following are great free choices for quickly probing WMI devices and getting information out of them quickly and free!
Our methodology for selecting WMI tools and software
We reviewed various WMI tools and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- Alerting and reporting capabilities
- Support for multi-tenant environments
- Ease of use, installation, and deployment
- A facility to analyze WMI status over time
- Graphical interpretation of data, such as charts and graphs
- A free trial period, a demo, or a money-back guarantee for no-risk assessment
- A good price that reflects value for money when compared to the functions offered
Paessler PRTG is a bundle of monitoring tools and it includes a WMI message collector that stores records for future reference in log files. The WMI sensor summarizes recent events, creating an easy-to-read status page. Stored data can be accessed for historical analysis.
Key Features:
- Agentless operations: PRTG doesn’t interact with the WMI system but simply collects circulating notifications
- Collects multiple metrics: Provides more than 50 pre-configured collectors
- Alerts for Windows services: Get notifications about service response problems
- Watches the operating system: Notes blocked services and abandoned processes
- Performance thresholds: Alerts for poor performance

Why do we recommend it?
Paessler PRTG is a useful package for system-wide IT asset monitoring, of which WMI monitoring is a part. The WMI service is useful when implemented in conjunction with other server monitoring tools in the package. WMI is only implemented in Windows but the PRTG package also includes sensors for monitoring Linux, so the package is able to monitor a multi-platform business system.
The WMI sensors are easy to set up and they provide default screens. Those dashboard screens can be customized and it is also possible to create new, extra screens in the console. Other units in the package will monitor applications, such as databases and Web servers and combining the information gleaned from WMI with other system performance feedback can help to keep a system running without errors.
Who is it recommended for?
This package will interest any business. It is scaleably priced, with a rate that is linked to the number of sensors that a buyer wishes to activate. Small businesses can use the system for free if they only activate 100 sensors. The PRTG package provides full-stack observability with monitoring options for networks, servers, and applications and it is centered on a network discovery service.
Pros:
- Suitable for all sizes of businesses
- Sensors for Linux monitoring as well as WMI for Windows
- Units for network, server, and application monitoring
- Metrics storage for historical analysis
- Troubleshooting tools with root cause analysis
You can register for a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Paessler PRTG is our top pick for a WMI tool as this package is able to collect more than 50 metrics from the WMI system. The package collects WMI messages without weighing on the processors of the hosts that emit these messages. The PRTG service stores WMI messages in log files for later access in historical analysis exercises. The full PRTG package includes sensors for network, server, and application performance monitoring. The package offers a free service to those who only want to activate 100 sensors. The tool is available as a software package for Windows Server and also as a SaaS platform on the cloud.
Download: Start a 30-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.paessler.com/wmi-monitoring
OS: Windows Server and cloud
2. WMI Explorer (CodePlex)
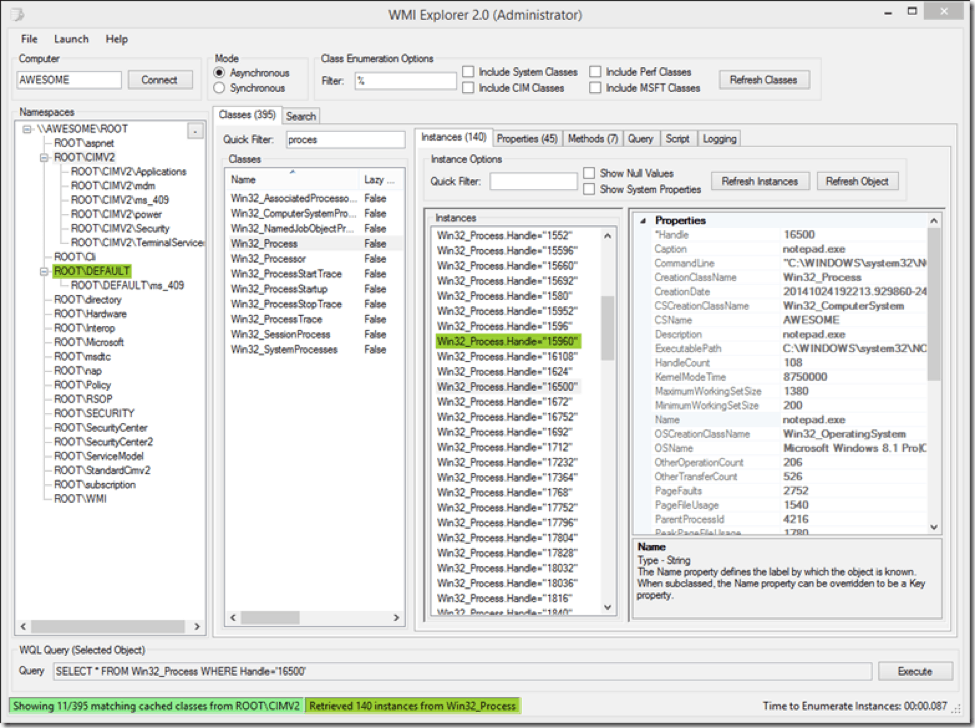
The WMI Explorer distributed by CodePlex is a top tool. It offers a modern, intuitive interface over what can be a very difficult to discern system.
Key Features:
- Query Assembler: Can execute complex queries and commands, so it will handle all the hard work for you.
- Comprehensive WMI Information: Gives you all the required information about WMI objects, so you can view quantifiers, properties, methods, WMI classes, and more.
- Export Capabilities: Export query results and WMI data in various formats to share to other users.
- Event monitoring: it helps admins to monitor WMI events related to log-in on systems and application events.
It exposes the WQL query to get your selected object or properties, as well as script generation to give you the corresponding PowerShell/VBScript to get them. This can be especially helpful when working with portions of the Windows system that PowerShell does not cover with Cmdlets yet.
One of our favorite features of this WMI Explorer is that it is free, so you can install it at will without having to worry about licensing.
Pros:
- Completely free
- Uses simple WMI queries
- Does a good job of simplifying large amounts of polled data
Cons:
- The interface could use improvement
Download:
https://wmie.codeplex.com/
3. WMI Explorer (Sapien)
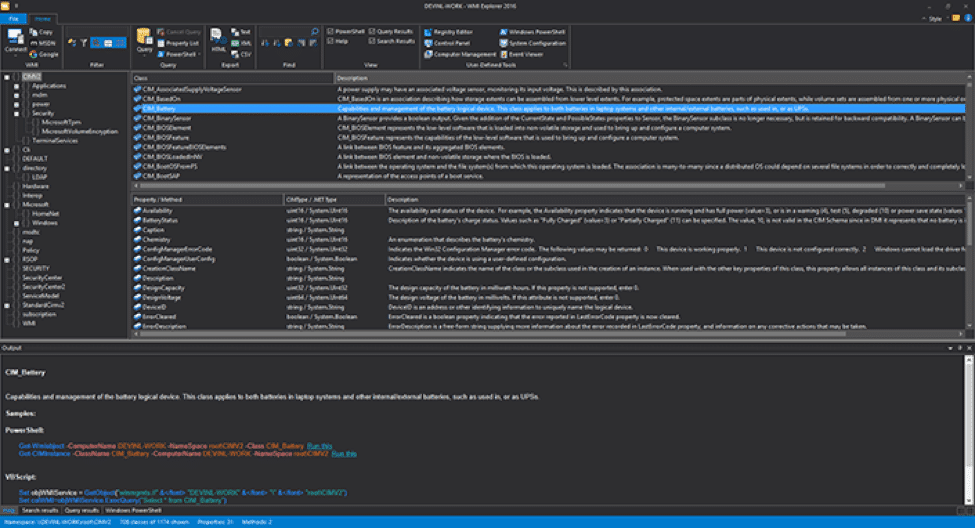
While not free, Sapien’s WMI Explorer exposes some very nice features that the CodePlex WMI Explorer does not. An excellent example is the integrated Technet button that will perform a search for your selected WMI object through Technet.
Key Features:
- Access All CIM Information: Easily access all CIM data and information stored in the database.
- Query Data: Uses a multi-threaded query function to browse query by class, custom CWL expressions, specific properties etc.
- Code Generation: Easily get the correct code for querying power scripts or VB scripts.
- Browse Remote Machine: Connect and browse various remote machines and search for queries in the CIM database.
The UI is also slightly more intuitive, with tabs at the bottom to show PowerShell and VBScript code to retrieve the selected item, along with an embedded PowerShell console for you to experiment with in-browser.
The UI also seems to be styled after the new Ribbon-based Microsoft Office menus, which can help provide a more familiar interface.
Pros:
- Easy to use and get started with
- The interface is familiar, closely resembling Windows Explorer
- Offers embedded PowerShell console for quick commands
- Generous 45-day free trial
Cons:
- Can take time to explore all features on the platform
Download:
https://www.sapien.com/software/wmiexplorer
4. WMI Explorer (Marc van Orsouw)
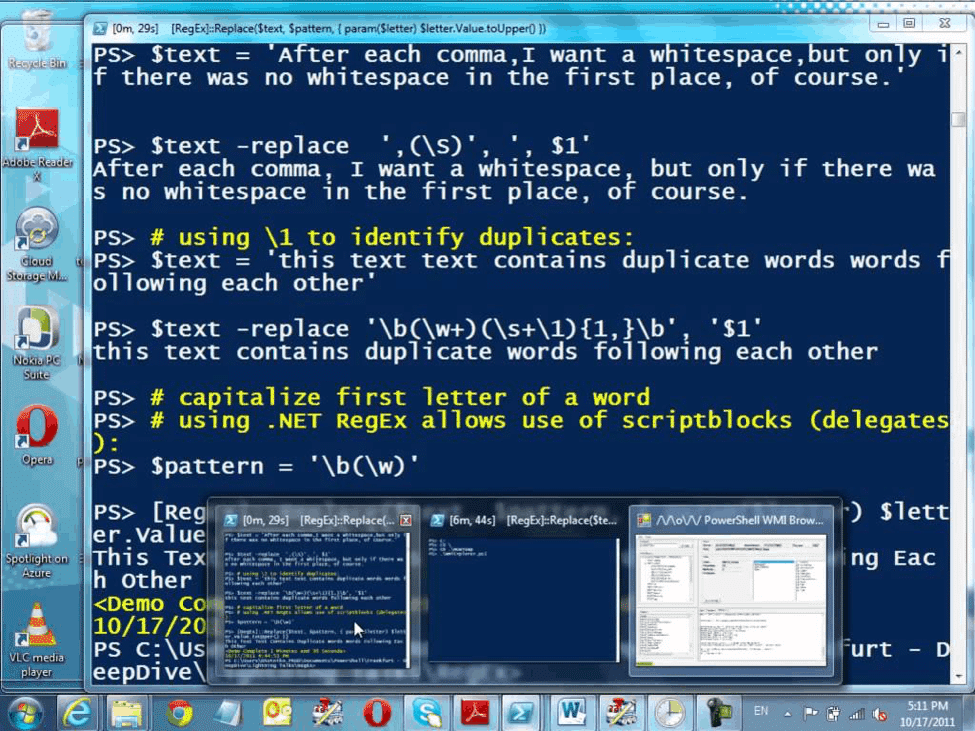
The big advantage of Marc van Orsouw’s WMI Explorer is that it is entirely PowerShell-based, meaning that it should run on any Windows Server 2008 or newer operating system without needing any installation. This can be a big advantage if you want to put a WMI Explorer on all of your systems, or if you just want to take a quick peak at a WMI object without needing to go through a hefty install process.
Key Features:
- Mines WMI Messages Across a Network: Users can collect WMI data from multiple computers across the network and identify problems from various machines.
- PowerShell Scripts: Allows automating routine tasks, perform complex queries and manage WMI data. Users can write and run their own custom Powershell scripts.
- Explore WMI Properties: Gives detailed information about WMI properties hence users can make smart decisions based on the WMI data.
- Unified WMI Activity View: Simply collect data from different sources and merge them into files to see WMI network activity
Pros:
- Great interface
- PowerShell-based WMI with GUI option
- Can run on any modern Windows server
Cons:
- Competing products offer similar features for free
Download:
http://powershell.org/wp/2013/03/08/wmi-explorer/
5. PowerShell
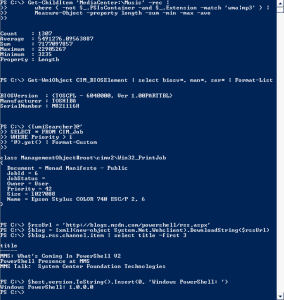
The other tools discussed are centered around finding WMI objects, but PowerShell is second to none when it comes to manipulating the objects once you’ve found them. This is heavily evidenced by the tight integration between PowerShell and the various WMI Explorers.
Key Features:
- Built-In Editor: Allows users to write, test, and debug their Powershell scripts.
- Extensible Addons: Comes with lots of keyboard shortcuts and extensible add-ons to use while writing scripts.
- Intellisense Tab: Can highlight syntax and get context-sensitive help.
- OMS Automation: Seamlessly use and manage powershell resources like DSC configurations and DSC nodes from one place to another.
When combined with information about the attributes from one of the WMI Explorers, PowerShell is the easiest way to programmatically access the underlying data from a local or remote WMI store.
Why do we recommend it?
PowerShell is a powerful scripting language and it has direct access to the Windows operating system. The service is able to deliver Windows services as well as query statuses. The tool can be a little dangerous as well because it can provide hackers access to important operating system values.
Who is it recommended for?
PowerShell is an important tool for systems administrators that like to create their own scripts. This is a great deal more powerful than batch scripts. The system can also be used to construct the classic features of monitoring services, such as alerts and automated responses.
Pros:
- Completely free
- Widely used and documented
- Extremly lightweight
- Part of Windows Server
Cons:
- Not the best option for those wanting a GUI
Download:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/
Conclusion
There is no shortage of tools at the administrator’s fingertips for working with WMI objects.
In the Windows world, WMI is often replacing SNMP as the protocol of choice for monitoring. The ability to see information about a remote system easily, and to combine that with centralized administrative software make WMI and important part of the administrators toolkit.
We’ve gathered some of the Best WMI Monitor Tools & Software of 2025 for you to use in your network and scripting environments, if we’ve missed any, please feel free to send us an email and we’ll update the post asap!
WMI Tools FAQs
What are some common features of WMI tools?
Common features of WMI tools include querying and retrieving system information, configuring system settings, and monitoring system performance.
What are some common WMI tools?
Common WMI tools include Solarwinds Free WMI Monitor, Windows Management Instrumentation Tester (wbemtest), WMI Explorer, and PowerShell.
How can WMI tools be used for system administration?
WMI tools can be used for system administration tasks such as configuring system settings, troubleshooting issues, and monitoring system performance.
What types of system information can be retrieved using WMI tools?
System information that can be retrieved using WMI tools includes hardware and software configuration, network settings, and system performance data.
What are some best practices for using WMI tools?
Best practices for using WMI tools include securing WMI communications using encryption and authentication, limiting user access to sensitive data, and regularly reviewing access logs and activity.
What is the role of WMI in Microsoft System Center?
WMI is a core component of Microsoft System Center for managing and monitoring system information, and is used by various System Center components such as Configuration Manager and Operations Manager.

Our website relies on funding from our readers, and we may receive a commission when you make a purchase through the links on our site.
The Best WMI Tools & Software for Windows Management Instrumentation Administration!
by NMS Admin - Last Updated: July 18, 2024
Here is our list of the best WMI tools & software for Windows management instrumentation administration:
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Windows Management Instrumentation, or WMI, is is a technology which enables easier management of Microsoft Windows-based servers and workstations. It collects and reports on configuration information about the computer using a standard interface. You get:
Our favorite WMI tools are broken into two categories:
As the names support one category is for browsing WMI objects and the other is for making changes.
The Best WMI Monitoring Tools
There are countless WMI tools, but the following are great free choices for quickly probing WMI devices and getting information out of them quickly and free!
Our methodology for selecting WMI tools and software
We reviewed various WMI tools and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
1. Paessler PRTG – FREE TRIAL
Paessler PRTG is a bundle of monitoring tools and it includes a WMI message collector that stores records for future reference in log files. The WMI sensor summarizes recent events, creating an easy-to-read status page. Stored data can be accessed for historical analysis.
Key Features:
Why do we recommend it?
Paessler PRTG is a useful package for system-wide IT asset monitoring, of which WMI monitoring is a part. The WMI service is useful when implemented in conjunction with other server monitoring tools in the package. WMI is only implemented in Windows but the PRTG package also includes sensors for monitoring Linux, so the package is able to monitor a multi-platform business system.
The WMI sensors are easy to set up and they provide default screens. Those dashboard screens can be customized and it is also possible to create new, extra screens in the console. Other units in the package will monitor applications, such as databases and Web servers and combining the information gleaned from WMI with other system performance feedback can help to keep a system running without errors.
Who is it recommended for?
This package will interest any business. It is scaleably priced, with a rate that is linked to the number of sensors that a buyer wishes to activate. Small businesses can use the system for free if they only activate 100 sensors. The PRTG package provides full-stack observability with monitoring options for networks, servers, and applications and it is centered on a network discovery service.
Pros:
Cons:
You can register for a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Paessler PRTG is our top pick for a WMI tool as this package is able to collect more than 50 metrics from the WMI system. The package collects WMI messages without weighing on the processors of the hosts that emit these messages. The PRTG service stores WMI messages in log files for later access in historical analysis exercises. The full PRTG package includes sensors for network, server, and application performance monitoring. The package offers a free service to those who only want to activate 100 sensors. The tool is available as a software package for Windows Server and also as a SaaS platform on the cloud.
Download: Start a 30-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.paessler.com/wmi-monitoring
OS: Windows Server and cloud
2. WMI Explorer (CodePlex)
The WMI Explorer distributed by CodePlex is a top tool. It offers a modern, intuitive interface over what can be a very difficult to discern system.
Key Features:
It exposes the WQL query to get your selected object or properties, as well as script generation to give you the corresponding PowerShell/VBScript to get them. This can be especially helpful when working with portions of the Windows system that PowerShell does not cover with Cmdlets yet.
One of our favorite features of this WMI Explorer is that it is free, so you can install it at will without having to worry about licensing.
Pros:
Cons:
Download:
https://wmie.codeplex.com/
3. WMI Explorer (Sapien)
While not free, Sapien’s WMI Explorer exposes some very nice features that the CodePlex WMI Explorer does not. An excellent example is the integrated Technet button that will perform a search for your selected WMI object through Technet.
Key Features:
The UI is also slightly more intuitive, with tabs at the bottom to show PowerShell and VBScript code to retrieve the selected item, along with an embedded PowerShell console for you to experiment with in-browser.
The UI also seems to be styled after the new Ribbon-based Microsoft Office menus, which can help provide a more familiar interface.
Pros:
Cons:
Download:
https://www.sapien.com/software/wmiexplorer
4. WMI Explorer (Marc van Orsouw)
The big advantage of Marc van Orsouw’s WMI Explorer is that it is entirely PowerShell-based, meaning that it should run on any Windows Server 2008 or newer operating system without needing any installation. This can be a big advantage if you want to put a WMI Explorer on all of your systems, or if you just want to take a quick peak at a WMI object without needing to go through a hefty install process.
Key Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Download:
http://powershell.org/wp/2013/03/08/wmi-explorer/
5. PowerShell
The other tools discussed are centered around finding WMI objects, but PowerShell is second to none when it comes to manipulating the objects once you’ve found them. This is heavily evidenced by the tight integration between PowerShell and the various WMI Explorers.
Key Features:
When combined with information about the attributes from one of the WMI Explorers, PowerShell is the easiest way to programmatically access the underlying data from a local or remote WMI store.
Why do we recommend it?
PowerShell is a powerful scripting language and it has direct access to the Windows operating system. The service is able to deliver Windows services as well as query statuses. The tool can be a little dangerous as well because it can provide hackers access to important operating system values.
Who is it recommended for?
PowerShell is an important tool for systems administrators that like to create their own scripts. This is a great deal more powerful than batch scripts. The system can also be used to construct the classic features of monitoring services, such as alerts and automated responses.
Pros:
Cons:
Download:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/
Conclusion
There is no shortage of tools at the administrator’s fingertips for working with WMI objects.
In the Windows world, WMI is often replacing SNMP as the protocol of choice for monitoring. The ability to see information about a remote system easily, and to combine that with centralized administrative software make WMI and important part of the administrators toolkit.
We’ve gathered some of the Best WMI Monitor Tools & Software of 2025 for you to use in your network and scripting environments, if we’ve missed any, please feel free to send us an email and we’ll update the post asap!
WMI Tools FAQs
What are some common features of WMI tools?
Common features of WMI tools include querying and retrieving system information, configuring system settings, and monitoring system performance.
What are some common WMI tools?
Common WMI tools include Solarwinds Free WMI Monitor, Windows Management Instrumentation Tester (wbemtest), WMI Explorer, and PowerShell.
How can WMI tools be used for system administration?
WMI tools can be used for system administration tasks such as configuring system settings, troubleshooting issues, and monitoring system performance.
What types of system information can be retrieved using WMI tools?
System information that can be retrieved using WMI tools includes hardware and software configuration, network settings, and system performance data.
What are some best practices for using WMI tools?
Best practices for using WMI tools include securing WMI communications using encryption and authentication, limiting user access to sensitive data, and regularly reviewing access logs and activity.
What is the role of WMI in Microsoft System Center?
WMI is a core component of Microsoft System Center for managing and monitoring system information, and is used by various System Center components such as Configuration Manager and Operations Manager.